Rubber moulding is a process which takes an elastomer or a compound of uncured, raw rubber and places it into aluminium or steel moulds using either injection, transfer or compression.
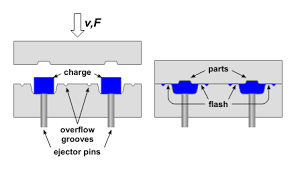
The rubber is then combined with heat and pressure to create a chemical reaction called curing or vulcanisation which makes the polymer chains contained within the rubber cross-link to turn the rubber into a usable product. Using pressure and heat in this process is vitally important as the chemical reaction would not occur without it.
Manufacturers can either use natural or synthetic rubber in this process as synthetic rubbers such as neoprene, silicone or ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) have very similar properties to natural rubber. Synthetic rubbers also have the advantages of greater durability, flexibility and endurance. All manufacturers of rubber products use the same injection, transforming or compression process to make a standardised rubber moulded product that is usable in many different industries.
How is rubber moulded?
The three rubber manufacturing processes are rubber injection moulding, transfer moulding and compression moulding. Rubber injection moulding defines a process in which rubber is heated and injected into a closed mould under high pressure. It has a number of benefits, including fast production times, a reduced level of rubber wastage and the ability to mould rubber into many different shapes and sizes.
Compression moulding pressurises and heats the rubber into a mould. This is a less expensive method, but it is slower than injection moulding.
Transfer moulding is similar to injection moulding in that rubber is pressurised into a mould system using heat to start the chemical reaction. All these manufacturing methods do have some HSE risks attached. For rubber moulding in the UK, specialists such as www.meadex.co.uk/rubber-moulding/ offer various custom-designed rubber moulded products.

Which industries use rubber moulding?
As rubber is such a versatile material, there are countless industries which take advantage of its limitless design options. Notable examples include the aerospace and automotive industries, which use rubber seals, gaskets, shock absorbers and tyres. Rubber moulding is also used in many appliances, consumer goods and electronics.
